Discover the differences between centrifugal and lobe pumps. Learn their advantages, applications, and which type best suits your industry needs.
Understanding the Differences Between Centrifugal and Lobe Pumps
Choosing the right pump is crucial for efficient fluid management across various industries. Among the most common types, centrifugal pumps and lobe pumps serve distinct purposes based on application needs. This article explores their operating principles, key differences, advantages, disadvantages, and ideal uses.
How Lobe Pumps Work
Lobe pumps operate on the positive displacement principle, moving fixed volumes of fluid per rotation. They are commonly used in industries requiring gentle fluid handling, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. These pumps excel at handling viscous materials with minimal shear force.
Their design features rotating lobes that create suction, drawing fluid into the chamber before steadily discharging it. With rotational speeds ranging from 120 to 600 rpm, lobe pumps ensure smooth flow, reducing the risk of damaging sensitive components. This makes them ideal for processing thick or delicate substances.
Advantages of Lobe Pumps
✔ Efficient for viscous and fragile liquids – Low shear force protects fluid integrity.
✔ Consistent performance – Operates efficiently despite pressure variations.
✔ Handles high-solid-content fluids – Suitable for slurries and pastes.
Lobe pumps can handle up to 1,000,000 centipoises viscosities, making them perfect for applications such as food pastes, heavy oils, and adhesives. Their self-priming capability allows them to operate without the need for liquid priming.
How Centrifugal Pumps Work
Centrifugal pumps function differently. They use centrifugal force to move fluids. A rapidly rotating impeller generates velocity, propelling liquids through the system. These pumps are widely used for high-volume fluid transfer applications, such as water distribution, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
With speeds ranging from 500 to 5000 rpm, centrifugal pumps efficiently manage high flow rates—often exceeding 100 m³/h—but their efficiency drops with highly viscous fluids.
Advantages of Centrifugal Pumps
🌊 High-volume capacity – Ideal for large-scale operations.
🤖 Versatile applications – Handles chemicals, abrasives, and water.
⚙ Lower maintenance costs – A Simpler design reduces upkeep.
These advantages make centrifugal pumps a cost-effective choice, particularly for low-viscosity fluids in continuous-flow systems.
Key Differences Between Lobe and Centrifugal Pumps
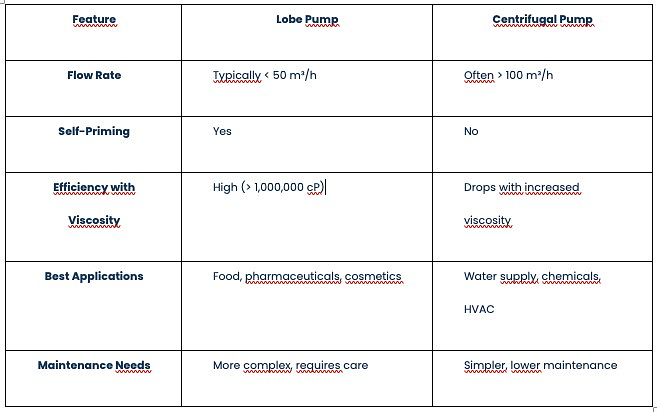
Choosing the Right Pump for Your Needs
The decision between a lobe pump and a centrifugal pump depends on several factors:
- Fluid properties – Lobe pumps are best suited for handling High-viscosity or shear-sensitive fluids, while centrifugal pumps suit low-viscosity liquids.
- Flow rate needs – Centrifugal pumps offer superior throughput for large-scale operations.
- Long-term costs – Lobe pumps may require higher maintenance but provide precise, gentle fluid handling.
By carefully evaluating these criteria, industries can select the most suitable pump for their operational needs.



